White Card PPE
When completing your general construction induction training (White Card course), you will be taught how to correctly fit and wear the following 4 pieces of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- hard hat
- hearing protection
- eye protection
- high visibility clothing
Note: If you decide to complete your QLD White Card course online (via Virtual Classroom/Zoom Meeting), you will be required to own or buy those 4 pieces of PPE in order to successfully complete the training.

General construction induction training - PPE signage
You can buy the PPE from most hardware stores. In Australia, Bunnings Warehouse is the most popular hardware store with 267 locations. Buying the required PPE for your White Card course from Bunnings Warehouse will cost just under $40.

Other construction PPE
Additional PPE may be necessary based on construction site, and should be addressed during site-specific safety induction.
PPE is anything that is being worn or used by workers to minimise the risk to their health and safety. Here is a non-exhaustive list of commonly used PPE:
- Boots
- Ear plugs
- Face masks
- gloves
- Goggles
- Hard hats
- High visibility clothing
- Respirators
- Safety harnesses
- Safety shoes
- Sunscreen
When assessing the suitability of PPE to the work task, you should consider:
- Match the PPE to the hazard, remembering that a work task may expose workers to more than one hazard. For example welders may need protection from harmful welding gases and fumes, as well as UV radiation, hot metal and sparks
- How the work is carried out and the level of risk to the worker. For example a more protective respirator may need to be worn where the level of air contamination is very high
- How long PPE will need to be worn
- Work demands of the work activity. For example the level of physical activity or dexterity required
- Make sure PPE that is to be worn at the same time can be used together
PPE must conform to the AS/NZS in Australia, which is a safety Standard developed jointly by Australia and New Zealand.
Hierarchy of risk control measures and PPE
As can be seen on the hierarchy of risk control measures chart, PPE should only be used as a last resort, as an interim measure or as a back-up.
The hierarchy of control measures can be applied in relation to any risk.
You must always aim to eliminate the risk, which is the most effective control. If this is not reasonably practicable, you must minimise the risk by working through the other alternatives in the hierarchy. These include substitution, isolation and engineering controls.
Administrative controls and PPE are the least effective at minimising risk because they do not control the hazard at the source and rely on human behaviour and supervision.
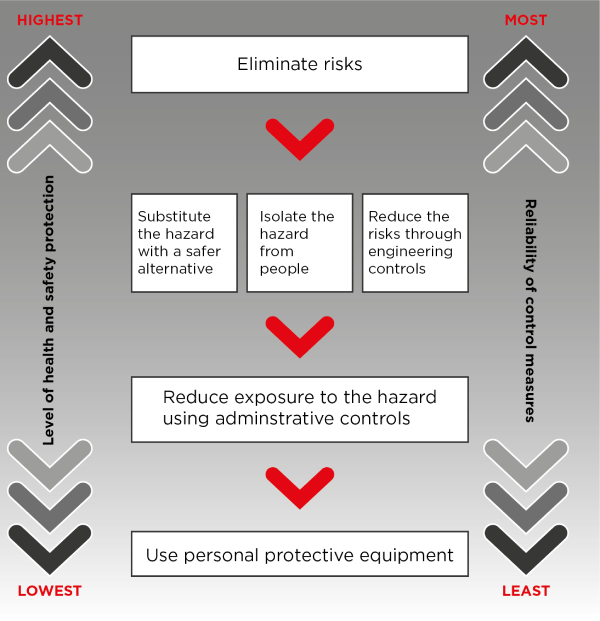
White Card - Hierarchy of control measures
Elimination example
An elimination example would be picking up rubbish and debris (trip hazards) on site and putting it in a designated skip bin. The hazard is now completely gone, making it the most effective risk control measure.
Substitution example
Substitution is the process of finding a better and safer alternative. For example, instead of using a ladder which, an elevated work platform could be substituted to reduce the fall hazard. The hazard still exists, but has been minimised substantially.
Isolation example
Isolation control means physically separate the hazard from people by placing barriers around a trip hazard for example.
Engineering controls example
An engineering control is a control measure that is physical in nature, including a mechanical device or process. For example, use mechanical devices such as trolleys or hoists to move heavy loads.
Administrative controls example
Administrative control measure include using safe work documentation such as job safety analyses (JSA) and safe work method statements (SWMS) to reduce exposure to hazards.
PPE
PPE is the last resort before the hazard reaches your body.
Who is responsible for the PPE?
Broadly speaking, employers are responsible for providing the PPE as well as the training, while employees are responsible to follow instructions, guidelines and to maintain the PPE in good working order.
Employer duty in regards to PPE
- Provide appropriate PPE
- Provide training on the use of PPE
- Replace or repair broken or damaged PPE
- Replace expired PPE (eg. hard hats should be replaced every 2-3 years)
- Make sure employees have access to correctly sized PPE
Employee duty in regards to PPE
- Wear PPE as instructed or displayed
- Keep the PPE in good working order by cleaning/servicing it
- Use PPE that fits properly
- Ask for clarification when
Looking to book a QLD White Card course? Visit our Queensland White Card booking page
